Nation states are facing a second wake-up call in public diplomacy. The first wake up call, prompted by the 9/11 attacks, was the realization that perceptions of foreign publics have domestic consequences. The second wake up call, which rang out first for China during the 2008 Olympics, and then for other countries with Wikileaks, the Arab Spring, and Occupy Movement, is that adversarial publics are able to challenge states in the quest for global public support. How states can effectively respond to this second wake-up call is a pressing area of public diplomacy research.
States appear to be viewing public diplomacy (PD) through a geopolitical lens and are focusing on other states as their primary competitors. However, viewed through a strategic communication lens, the greatest PD competition and threat to states are not other states, but rather initiatives by adversarial publics. Aside from challenging individual states, the diversity of political affinities and cultural identities of these publics raise questions about whose ‘norms’ and ‘rules’ should govern how issues are addressed in the global public arena. This has implications for all states.
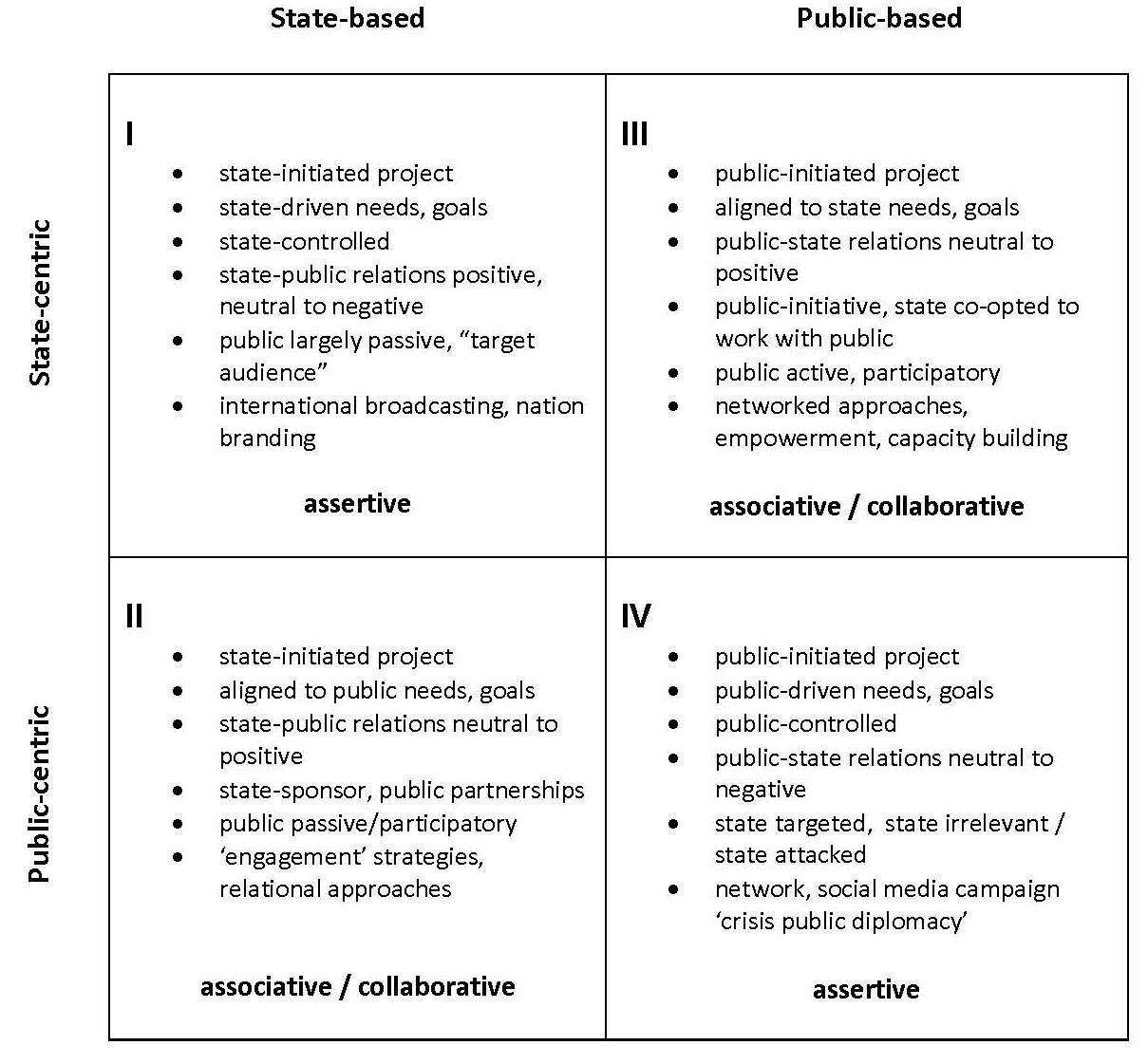
To begin to address this challenge, public diplomacy needs a more nuanced understanding of publics beyond non-state actors. The international relations (IR) literature tend to use the terms “state-based” and “state-centric” interchangeably to distinguish domains of state actors from non-state actors. In communication, the term “audience-centric” is used specifically to distinguish between communication messages and approach designed around the audience’s needs, interests and goals and those of the sponsor. Whereas much of PD has highlighted (soft) power, messages, or images, the PD Quadrants below highlight the importance of the relational dimension between states and publics in considering strategic PD options.
State-based Public Diplomacy
PD Quadrant I reflects the traditional view of public diplomacy as a state-based, state-centric activity. It is state-based in that the initiative is designed, implemented and controlled by the state. It is state-centric in that PD initiatives are designed to meet the interests, needs and goals of the state.Relations with publics are often obscured by the focus on getting the message out and promoting the state’s interests. Because the public is viewed as passive, the relational dimension is often unexplored. However, if relations are positive, the message and image of the state tends to be favorably received. If relations are negative, the state’s communication efforts tend to encounter unexpected resistance. International broadcast and nation branding campaigns reflect the state-based, state-centric public diplomacy of PD Quadrant I.
PD Quadrant II represents a shift from state-centric to public-centric initiatives. Initiatives are still state-based in the sense that it is the state that initiates, sponsors the initiative. However, despite state control over the initiative, public participation and building positive relations is viewed as pivotal feature for PD initiatives in PD Quadrant II. To secure public participation and build relations, rather than being primarily focused on the state-centric needs or goals, the PD initiative’s message, approach and selection of media platforms are designed to resonate positively with the public. The rise of the “new public diplomacy” over the past decade that advocate a more “relational” approach and the view of public diplomacy as “engagement” exemplify the state-based, public-centric initiatives in PD Quadrant II.
Reversing the Role of the Public
PD Quadrant III represents a shift from state-based to public-based initiative. Digital media have effectively enable publics to reverse communication roles with the state. Rather than being a consumer of state-generated information, publics are able to generate communication for state attention and consumption. Whereas the state-based, public-centric initiatives in PD Quadrant II seek to co-opt the public, the public-based, state-centric projects in PD Quadrant III seek to co-opt and involve the state. Many of the global, complex issues such as global warming, health, and education originally launched by public such as the Campaign to Ban Landmines, are illustrative of PD Quadrant III.
What both PD Quadrant II and III have in common is a neutral to positive relations between state and publics. Publics are often called “stakeholders,” and assume organized public representatives such as civil societies or nongovernmental organizations (NGOs). There is also an implicit assumption that the state and the public share similar goals and perspectives. The positive relations and shared perspectives lie behind the willingness to adapt messages and approaches, build relations or networks, seek commonality, mutual engagement, dialogue, and potential collaboration.
Adversarial Public Stakeholders
PD Quadrant IV is distinguished from other quadrants by the public’s capacity to produce PD content and neutral to negative relations with the state. PD initiatives are public-based in the sense that the public retains primary if not exclusive control over the initiative. The initiatives are public-centered in that they are designed to meet the needs, interest and goals of the public, which may be framed as neutral or counter to those of the state. Rather assuming positive relations with publics, states may be faced with adversarial public stakeholders.While often overlooked, these public stakeholders may be even more strategic stakeholders in public diplomacy initiatives.
Becauseadversarial stakeholders continue to retain a strong vested interest in a contested public issue, they cannot be dropped from the PD equation even ifthey disagree with the state. Nor can they be dismissed as “irrational.” These adversarial stakeholders may commandmore perceivedcredibility and legitimacy by the public than the state.Attempts to openly challenge these stakeholders canfurther serve to alienate the state. The state may struggle for relevancy. Most importantly, thesestakeholders are provingadept at usingdigital tools and network communication strategies to generate a soft power differentialcapable ofchallengingstates. They can command state attention.
For states, PD Quadrant IV represents the challenge of “crisis public diplomacy.” Unlike the relatively stable communication with benign publics, crisis public diplomacy entails communicating simultaneously with multiple publics – not just foreign or domestic, but favorable and adversarial publics – in a highly visible, rapidly evolving, contested public arena.
Whither Public Diplomacy?
In theory, if not entirely yet in practice, states have gotten the first wake up call. The need to shift from state-centric to more participatory and relational public-centric approaches is evident in the accelerated use of social media in public diplomacy.
States may be less appreciative of the full implications of the second wake-up call, or shift from state-based to public-based initiatives. Recent PD reports(Hocking et al. 2012; Hanson 2012) reflect the trend of discussing public diplomacy in terms of (soft power) competition from other countries. However, the majority of the threats raised in the reports are not from other countries, but from adversarial public stakeholders in PD Quadrant IV.
In looking ahead to the future of public diplomacy, states need to move quickly beyond whether and how to use the social media for public-centric initiatives. As mentioned in the soft power differential, the greatest potential threat that states face is being blind-sided by a highly-network non-state actor. Already this has happened for several states. Understanding the dynamics and developing strategies for adversarial public-basedPD Quadrant IV is one of the most urgent and pressing area of public diplomacy scholarship.
—
R.S. Zaharna is a full-time professor of Public Communication at American University. She specializes in intercultural and international strategic communication, with an emphasis on culture and communication in the Arab and Islamic regions. Her most recent book is Battles to Bridges: US Strategic Communication and Public Diplomacy after 9/11 (Palgrave-Macmillan, 2010).
References
Brian Hocking, Jan Melissen, Shaun Riordan and Paul Sharp. Futures for diplomacy: Integrative Diplomacy in the 21st Century. Clingendael Report No. 1, Clingendael, Netherlands Institute of International Relations, October 2012.
Fergus Hanson, Baked In and Wired: eDiplomacy@State, Policy Paper No. 30, Brookings Institute, Washington, DC, October 2012.
Further Reading on E-International Relations
- The Semi-Public World of Influencer Diplomacy, Universities and Think Tanks
- Public Diplomacy: China’s Newest Charm Offensive
- The Limits of Soft Power-Sports Diplomacy Templates in IR Research
- Opinion – The Concept of Soft Power and AI
- Reflecting on the 75th Anniversary of Indonesian-Turkish Relations
- Opinion – How Iranian Women Are Charting the Course for Freedom