
This is an excerpt from Crisis in Russian Studies? Nationalism (Imperialism), Racism and War by Taras Kuzio. Get your free download from E-International Relations.
Since 1991, there has been an in-built tension in Russian-Ukrainian relations, because ‘the more Ukraine asserted its sovereignty, the more Russia questioned it, and vice versa’ (D’Anieri 2019, 63). The 2014 crisis cannot be understood without ‘looking at its long-term sources’ because to do so would be to tackle them ‘out of context and therefore to misinterpret them’ (D’Anieri 2019, 253). The sources of the 2014 crisis lie in Russia’s inability to recognise Ukraine and Ukrainians, which hark back to the early 1990s. The 2014 Russian-Ukrainian crisis is not fundamentally different from the many disagreements the two sides have had since December 1991 (D’Anieri 2019, 265–266).
This chapter is divided into two sections. The first section analyses the impact of Russian annexation and military aggression on the disintegration of Ukraine’s ‘east,’ which comprised eight southeastern Ukrainian oblasts prior to 2014; the replacing of the Soviet concept of Russians and Ukrainians as close, but different ‘brothers’ with the Tsarist Russian and White émigré denial of Ukraine and Ukrainians, which particularly impacted upon Russian-speaking eastern Ukrainians; and the collapse in Russian soft power in Ukraine. The second section discusses the prospects for a peaceful settlement of the Russian-Ukrainian War. Former President Poroshenko was never the obstacle to peace, and President Zelenskyy will not become the harbinger of peace because the roots of the Russian-Ukrainian War do not lie in the choice of Ukrainian president, but rather in Russian nationalist (imperialist) attitudes towards Ukraine and Ukrainians, which will remain as long as Putin is de facto president for life.
Impact of the War
Pro-Russian Ukrainian ‘East’ is No More
Russian-speaking southeastern Ukrainians have undertaken the majority of the fighting against Russian and Russian proxy forces, and they account for the highest rate of casualties of Ukrainian security forces. Over two million IDPs and refugees are Russian speakers from the Donbas. Russia is not fighting ‘western Ukrainian nationalists,’ but is primarily killing, wounding, and harming Russian-speaking Ukrainians. Eastern Ukraine has the highest proportion of military veterans and the highest rate of casualties among Ukrainian security forces (see 6.2 map).
6.1. Photographs in Kyiv and Dnipropetrovsk Oblast of Ukrainian Security Forces Killed in the Russian-Ukrainian War.
Source: Author’s photographs.
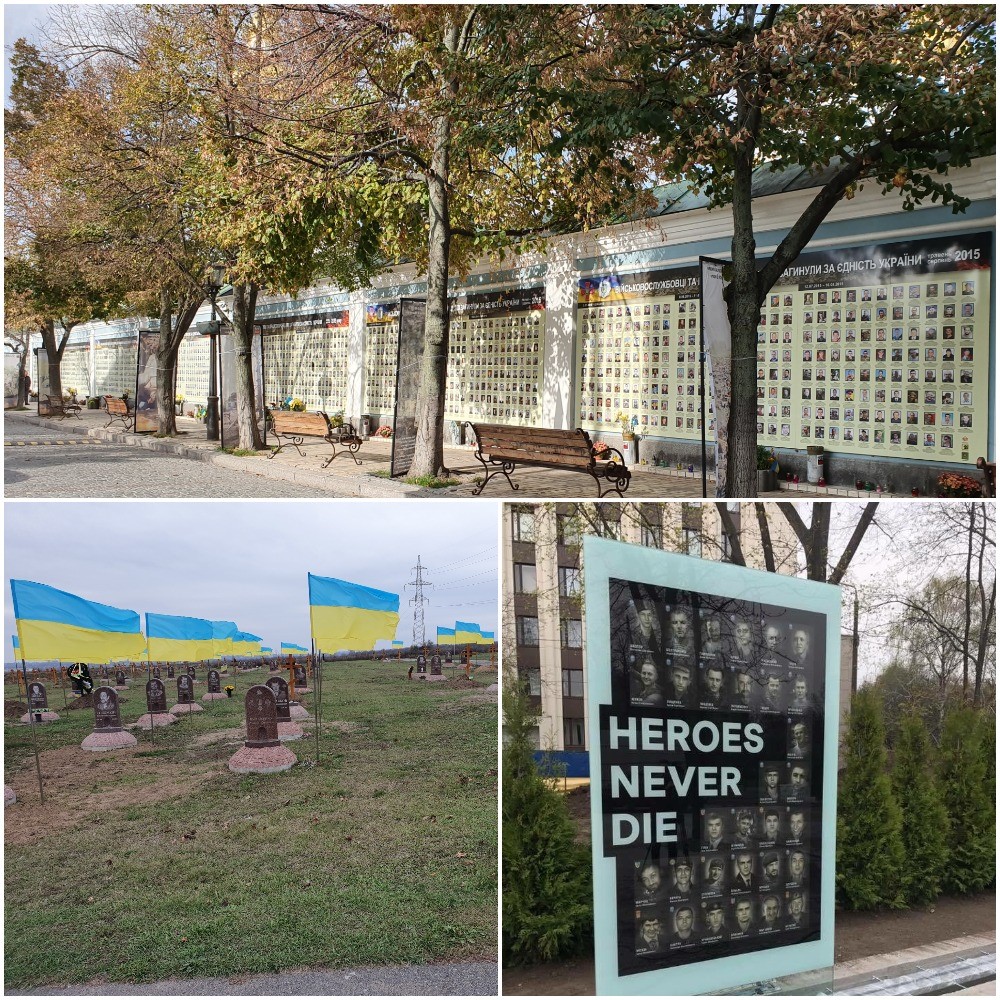

Note: Top photograph:long wall alongside Kyiv’s Mykhayivskyy Zolotoverkhnyy Monastyr (St. Michael’s Golden-Domed Monastery) with photographs of Ukrainian security forces killed in the Russian-Ukrainian war; bottom left photograph: one section of the large military cemetery in the city of Dnipro of Ukrainian security forces killed in the Russian-Ukrainian war; bottom right photograph: one of the many glass obelisks in the Alley Heroyiv (Alley of Heroes) in the centre of the city of Dnipro dedicated to the Nebesna Sotnya (Heavenly Hundred) killed during the Euromaidan Revolution and Ukrainian security forces killed in the Russian-Ukrainian war.
Russian information warfare and Putinversteher scholars (Sakwa 2015, 2017; Cohen 2019) depict volunteer battalions as dominated by extreme right ideologies and western Ukrainians; in fact, they were largely filled by Russian speakers and national minorities (Aliyev 2020). Huseyn Aliyev (202) writes that ethnic nationalism was ‘one of the least probable causes of wartime mobilization.’ Azov and Pravyy Sektor battalions, the two battalions demonised for their ‘nationalist’ ideologies most often, included Georgians, Jews, Russians, Tatars, and Armenians.
6.2. Map of Ukrainian Security Forces Killed in the Russian-Ukrainian War by Oblast
Source: http://memorybook.org.ua/indexfile/statbirth.htm. Used with permission.
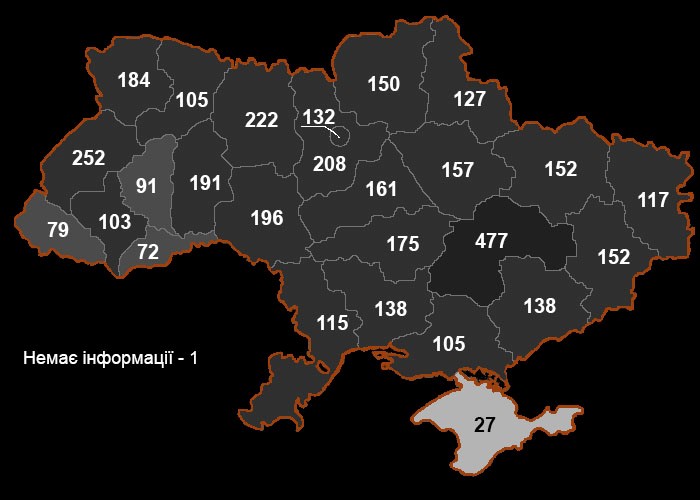
Note: Total of 4,270 known casualties as of 1 March 2020. Note the highest number of 477 casualties in Dnipropetrovsk oblast.
Six years of Russian military aggression have changed Ukraine, Ukrainian views of Russia, and Ukrainian-Russian relations. Russia’s annexation of Crimea and on-going military aggression in eastern Ukraine have two long-lasting consequences for scholarly research on Ukraine. The first consequence is the disappearance of a pro-Russian ‘east,’ and the second consequence is the collapse in Russian soft power. Since 2013, Russian policies have been counter-productive and have deepened Ukraine’s break with Russia.
Tatyana Zhurzhenko (2015, 52) writes that 2014 represented a ‘new rupture in contemporary history, a point of crystallization for identities, discourses, and narratives for decades to come.’ Ukraine’s fault line is no longer east versus west, but Ukraine versus the Donbas. Medical volunteer Natalya Zubchenko, based in the city of Dnipro, said, ‘We don’t think of ourselves as east or west. We’re central’ (Sindelar 2015). The fracturing of Ukraine’s ‘east’ and the reduction to two Donbas oblasts represent ground-breaking changes in Ukrainian identity and the country’s regional configuration (Zhurzhenko 2015; Kuzyk 2018; Kulyk 2016, 2018, 2019).
The collapse in pro-Russian sentiments and growth in Ukrainian patriotism in Dnipropetrovsk created a ‘domino effect,’ which spread to neighbouring regions because of the oblast’s industrial power and size. Opinion polls show that there is now a belt of four oblasts – Dnipropetrovsk, Zaporizhzhya, Kherson, and Mykolayiv – within the former eight pro-Russian oblasts of southeastern Ukraine that no longer hold pro-Russian views or pro-Russian foreign policy orientations. Changes in Kharkiv and Odesa were not as dramatic, but even there, pro-Russian sentiment has declined. Ukrainian identity is also growing in Ukrainian-controlled Donbas (Sasse and Lackner 2018; Haran, Yakovlyev and Zolkina 2018).
Russian speakers in Ukraine are loyal to a multi-ethnic country where the Russian and Ukrainian languages are both spoken and disloyal to the Russian World. This is reflected in three-quarters of Ukrainians describing the conflict as a Russian-Ukrainian War (Poshuky Shlyakhiv Vidnovlennya Suverenitetu Ukrayiny Nad Okupovanym Donbasom: Stan Hromadskoyii Dumky Naperedodni Prezydentskykh Vyboriv 2019). Russia’s invasion led Russian-speaking Ukrainian patriots to view DNR and LNR leaders as Russian puppets; that is, Russian proxies (Aliyev 2019).
Until 2014, centrist Ukrainian and Russian speakers were not anti-Russian and adhered to the Soviet concept of Ukrainians and Russians being closely related, but different ‘brothers.’ They would never accept the Tsarist Russian and White émigré view of Ukrainians as one of three branches of the ‘All-Russian People’ and the non-existence of a Ukrainian state.
Putinversteher scholars believe that peace can be achieved in the Donbas by Ukraine embracing its ‘bicultural’ Ukrainian-Russian identity (Petro 2015, 33). Hahn (2018, 176) agrees with Russian leaders that left- and right-bank Ukrainians and Russians are a ‘single nation,’ ‘having common historical roots and common fates, a common religion, a common faith, and a very similar culture, languages, traditions and mentality.’ The failure of Putin’s ‘New Russia’ project shows that Ukraine never had a ‘bi-cultural’ identity, and adopting Petro’s (2015) proposals would have been impossible prior to 2014 and, after six years of war and bloodshed, his proposal is illusory.
Low levels of Ukrainian allegiance to the Russian World were already evident before the 2014 crisis (Wawrzonek 2014) and in 2014. A majority of Ukrainians in southeastern Ukraine did not believe that they were part of the Russian World. Of Ukraine’s eight southeastern oblasts, the Russian World was thoroughly unpopular in Dnipropetrovsk, Zaporizhzhya, Kherson, and Mykolayiv, had only slightly higher support in Kharkiv and Odesa, and had the highest support in the Donbas. Overall, only 27.4% in southeastern Ukraine felt that they belonged to the Russian World (O’Loughlin, Toal and Kolosov 2016, 760). Russian military aggression ‘killed any appeal’ for the Russian World in Ukraine (Plokhy 2017, 345).
In spring 2014, Russia’s strategy to organise pro-Russian rallies that would capture official buildings, declare non-recognition of the Euromaidan government’s authority, and establish ‘people’s republics,’ which would seek protection through Russian military invasion, had low levels of support throughout southeastern Ukraine (The Views and Opinions of South-Eastern Regions Residents of Ukraine 2014). If Russia had invaded eastern Ukraine to ‘protect’ Russian speakers, only 7% in southeastern Ukraine would have greeted these Russian troops (The Views and Opinions of South-Eastern Regions Residents of Ukraine 2014).
Russians and Ukrainian are No Longer ‘Brothers
The 1863 thesis of tryedynstva russkoho naroda was revived in a refashioned form after 1934, when Ukrainians and Russians were presented as different, but at the same time close ‘brotherly peoples’ whose fate was forever bound together. During Putin’s presidency, Russian discourse and policies towards Ukraine stagnated from this Soviet ‘brotherly peoples’ concept to the Tsarist Russian and White émigré concept of tryedynstva russkoho naroda, which considers Ukraine an artificial state, Ukrainians and Russians as ‘one people,’ and Ukraine as including ‘Russian lands’ that were wrongly allocated by the Soviet regime. Such views have always had very limited support in Ukraine outside of Crimea and the Donbas.
It is also important to remember that sharp breaks in 1991 and 2014 followed changes that had taken place earlier. In 1991, the disintegration of the USSR and Ukrainian independence came after six years of civil strife, nationalist mobilisation, splits in the Soviet Communist Party of Ukraine, and opposition success in Soviet Ukrainian and local elections. The 2014 crisis similarly came after a quarter of a century of nation-building in an independent Ukrainian state, and the growing importance of national identity and memory politics following the Orange Revolution. Ukrainian nation-building progressed rapidly after 1991 and 2014, but this development had been set in motion by earlier periods of slower changes in identity.
The official Soviet historiography of Kyiv Rus as the joint inheritance of three eastern Slavs remained influential until the Orange Revolution. In a 2006 opinion poll asking which statement they supported, 43.9% of Ukrainians agreed that Ukrainian history was an integral part of eastern Slavic history, while 24.5% believed that Ukraine had exclusive title to Kyiv Rus (Rehionalni Osoblyvosti Ideyno-Politychnykh Orientatsiy Hromadyan Ukrayiny v Konteksti Vyborchoyi Kampanii 2006, 5). A decade later, this had changed, and 59% of Ukrainians believed that Kyiv Rus and other historical developments were exclusively Ukrainian, with 32% continuing to believe that Ukrainian history is part of eastern Slavic history (Konsolidatsiya Ukrayinskoho Suspilstva: Vyklyky, Mozhlyvosti, Shlyakhy 2016). Two years later, another poll found that 70% of Ukrainians believed that Ukraine is the exclusive successor to Kyiv Rus (rising from 54% in 2008), with 9% disagreeing (Dynamics of the Patriotic Moods of Ukrainians 2018). Within twelve years, the number of Ukrainians who claimed exclusive title to Kyiv Rus history had nearly tripled from 24.5% to 70%.
Five years after Russia launched its military aggression against Ukraine, only voters for the pro-Russian Opposition Platform-for Life (88%) believed that Ukraine is part of eastern Slavic history. Most of these voters live in the shrunken ‘east’ of Ukrainian-controlled Donbas. Most voters for the Fatherland Party (Batkivshchina, 62%), Zelenskyy’s Servant of the People Party (Sluhu Narodu, 61%), Voice Party (Holos, 54%), and Poroshenko’s European Solidarity Party (Yevropeyska Solidarnist, 54%) do not believe that Ukrainian history is part of eastern Slavic history (Ukrayina Pislya Vyboriv: Suspilni Ochikuvannya, Politychni Priorytety, Perspektyvy Rozvytku 2019). Could we deduce from this that Zelenskyy’s voters are more ‘nationalistic’ than those who support Poroshenko?
The Soviet ‘brotherly peoples’ concept gave eastern Ukrainians and Russian speakers a Ukrainian identity and a close relationship to Russia. Russian-Ukrainian ‘brotherly’ relations were undermined by the rehabilitation of Tsarist Russian and White émigré views of Ukrainians, and by Russia’s annexation of Crimea and invasion of Ukraine. This was reflected in the outrage present in Anastastiya Dmytruk’s poem at the beginning of this book, which says that Russians will no longer be the brothers of ‘Ukrainians.’
Vasyl Kremen and Vasyl Tkachenko (1998, 18), two political consultants in President Kuchma’s team, stressed that unity in Kyiv Rus ‘does not mean “eternal unity” of the three eastern Slavic peoples.’ Plokhy (2017, 346) concludes, ‘The imperial construct of a big Russian nation is gone, and no restoration project can bring it back to life, no matter how much blood and treasure may be expended in the effort to revive a conservative utopia.’ By 2018, 66% of Ukrainians believed they had been brothers with Russians, but this was no longer the case, while another 16% believed that Russians and Ukrainians had never been brothers (Mishchenko 2018). This means that a high 82% of Ukrainians no longer view Russians as their ‘brothers’ (Kulchytskyy and Mishchenko 2018, 192).
The first nuclear bomb against Russian-Ukrainian ‘brotherly’ relations detonated around Crimea. Plokhy (2017, 345) writes: ‘The Russian World was now associated not just with Pushkin and the Russian language but with a land grab that had cost thousands of dead and wounded and disrupted millions of lives.’ Putin’s (2020c) claim that Russia’s annexation of Crimea was not the reason why relations with Ukraine were poor is untrue, because Crimea was one of the central components of the Soviet nationalities policy of Russian-Ukrainian ‘brotherhood.’ In 1954, the peninsula was transferred from the Russian SFSR to Soviet Ukraine on the symbolically important 300th anniversary of the reunion of Ukraine and Muscovy in the 1654 Treaty of Pereyaslav.
The second nuclear bomb detonated in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Putin chose Ukrainian Independence Day to invade Ukraine in 2014. Russian speakers who joined Ukrainian volunteer battalions viewed Russian-controlled Donbas as run by ‘gangsters’ that misrepresented Ukraine (Aliyev 2019). They were especially resentful at Russia’s invasion in August 2014, which for them crossed a ‘red line’ and turned the conflict into a Russian-Ukrainian War.
Putin offered ‘guarantees’ for the withdrawal of Ukrainian forces, who were surrounded by an invading Russian force. Putin lied and, near the Donetsk oblast town of Ilovaysk, Russian forces killed 366 Ukrainian soldiers, wounded 429, and took 300 prisoners. The General Prosecutor’s Office of Ukraine described Putin’s maskirovka as a war crime and sent the case to the Office of the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court. An additional war crime was ‘Russian servicemen and the irregular illegal armed formations under their control’ who murdered and wounded Ukrainian soldiers. Ilovaysk buried Ukrainian-Russian ‘brotherhood.’
15% of Ukrainian voters are veterans of the Donbas War or are family members of veterans. By the end of Putin’s term in office in 2036, a far higher proportion of Ukrainian voters will be veterans of the Donbas War. Veterans are very active in civil society and party politics.[1] Streets and roads have been renamed throughout Ukraine in honour of Ukrainian soldiers who have died fighting in the Donbas. New sections of cemeteries for casualties of Ukrainian security forces who died fighting in the Russian-Ukrainian War are now commonly found alongside graves of Soviet soldiers who fought in the Great Patriotic War and in Afghanistan, and Ukrainian nationalists who fought for the Western Ukrainian People’s Republic (ZUNR) and Ukrainian Insurgent Army (UPA). As of December 2019, 523 plots of Ukrainian soldiers killed in the Russian-Ukrainian can be found throughout Ukraine, containing a total 1,636 graves.
Military casualties and veterans of the war increase support for radical post-Euromaidan memory politics, breaking with Soviet and Russian interpretations of Ukrainian history and Ukraine’s divorce from Russia (Identychnist Hromadyan Ukrayiny v Novykh Umovakh: Stan, Tendentsii, Rehionalni Osoblyvosti 2016). In 2016, 69% of veterans, compared to 46% of Ukrainians overall, condemned the Soviet regime and backed the prohibition of communist symbols. Meanwhile, 58% of Donbas War veterans supported one of four de-communisation laws (Law No. 314-VIII) providing legal status and honouring those they consider to be their predecessors in the fight for Ukrainian independence (Identychnist Hromadyan Ukrayiny v Novykh Umovakh: Stan, Tendentsii, Rehionalni Osoblyvosti 2016). Veterans and soldiers of the Russian-Ukrainian War are largely in the 20–45 age group, which also makes them more radical proponents of Ukrainian identity and negative towards Russia. More Ukrainians under the age of 59 support (than oppose) one of the de-communisation laws banning communist and Nazi symbols and denouncing the USSR and Nazi Germany as totalitarian states. Only the 60–69 and above 70 age groups had higher numbers of opponents than supporters of de-communisation (Shostyy rik dekomunizatsii: stavlennya naselennya do zaborony symboliv totalitarnoho mynuloho 2020).
Russia’s invasion had its greatest impact upon eastern Ukrainians, such as Russian-speaking Anatoliy Korniyenko, whom I interviewed in the city of Dnipro in 2019 and 2020. His 22-year-old son Yevhen had been killed in the Russian-Ukrainian War on 12 August 2014, and Anatoliy Koniyenko volunteered for combat duty at the age of 58 (the last time he had served was in the Soviet army in the 1970s). He served four years on the Ukrainian-Russian front line. I asked him why he had enlisted, to which he replied, ‘I wanted revenge.’ There are very many Korniyenko’s in Ukraine, particularly in the east and south, who have lost loved ones to Russian military aggression or who have friends who have lost family members in the war.
6.3. Yevhen and Anatoliy Korniyenko, First Museum of the ATO in Dnipro and Donbas War Zone.
Source: Author’s photographs.

Note: On the left is a memorial to Yevhen Korniyenko (5 March 1992–12 August 2014) in the Pershyy Muzey ATO Dnipro (First Museum of the ATO in Dnipro). On the right is his father, Anatoliy Koniyenko, when he was in the Donbas war zone.
Another example of the re-thinking of Ukrainian attitudes brought about by the war can be found in Canadian-Ukrainian Andrew Fesiak. His father was one of a few who managed to escape a massacre perpetrated by Polish nationalist against his family and the majority of the inhabitants of a Ukrainian village in June 1945 on the current Polish-Ukrainian border. The irony is that Polish nationalists then did not view Ukraine as a real nation, similar to contemporary Russian nationalists. The leader of the Polish nationalist group, Józef Zadzierski (‘Wołyniak’), who committed the massacre, and many other crimes against the Ukrainian minority is considered a hero in Poland today.[2] Andrew Fesiak’s mother was one of the 150,000 Ukrainians who were ethnically cleansed in the spring 1947 Akcja Wisła (Operation Vistula) by the Polish communist authorities from southeastern Poland to the former German territories that had been included in post-war Poland.
Fesiak has lived in Kyiv for two decades and has a Ukrainian family. He comes from a town in Canada’s province of Ontario, where he attended the St. John the Baptist Ukrainian Orthodox Church. He went to Ukrainian school with children from the Ukrainian nationalist community, but had little in common with them ideologically or religiously (the nationalist community tended to be Greek-Catholic). When I met Fesiak for the first time in Toronto in 2001, he held mild pro-Soviet and pro-Russian views, which is no longer the case. Fesiak explained his gradual evolution prior to 2014 and his rapid change since then:
Various things that Russia did since Ukraine’s independence slowly changed my mind. First and foremost was their disrespect for everything Ukrainian. Russian efforts to constantly denigrate Ukraine, Ukrainians, and the language and culture was increasingly evident under Putin. I previously believed it would be in Ukraine’s interests to have a close economic relationship with Russia and other former Soviet countries as the world was forming into economic unions and the EU was not offering Ukraine membership. But Russia’s economic war against Ukraine proved they could not be trusted even in this area. When Yanukovych was in power, a language law was adopted that upgraded Russian to a de facto second state language, to the detriment of the Ukrainian language. Russian economic warfare against Ukraine continued, regardless of the fact that Yanukovych was pro-Russian. This annoyed me so much that when I went on a business trip to Moscow in 2012, I purposefully spoke Ukrainian instead of Russian.
The point of no return was Russia’s annexation and invasion in 2014. This was a real stab in the back that no generation of Ukrainians would ever forget. The fact they could do this in the twenty-first century in Europe just blew my mind. Russia’s military aggression forced me to re-examine every episode of Ukrainian history and its relations with Russia. Prior to Russia’s invasion, when looking at history, I may have said sure, ‘that’ particular negative historical event happened, but it was a long time ago and times have changed.
After Russia’s annexation and invasion, I see that what Russia did in 2014, was a continuation of their ‘normal’ state of affairs, which they have been doing for centuries. I was also shocked and dismayed by another big stab in the back from the Russian people themselves, with 85% of them supporting the Kremlin’s treacherous act of stealing Crimea from Ukraine. This is just as bad, if not worse, than the actual invasion and annexation, in terms of Ukrainians being betrayed by their so-called ‘brothers.’ It’s one thing for a government to commit a crime, it’s another thing when their citizens massively support that crime, especially against a country and people that they consider to be their ‘brothers.’
Collapse in Russian Soft Power
The disintegration of Ukraine’s pro-Russian ‘east’ is part of an overall implosion of Russian soft power influence in Ukraine (Zarembo 2017, 47). In September 2014, Ukraine ended the broadcasting of Russian television channels (Ukrainian State Film Agency 2014) and, from 2016, began curtailing imports of banned Russian books and films (Ukrainian Parliament 2016a; Ukrainian State Film Agency 2016). From 2017, Ukraine banned the entry of Russians deemed a threat to Ukrainian national security. Russian social media and some online sources, such as the Russian internet search engine Yandex, the Russian equivalent of Facebook VKontakte, Odnoklassniki, and email domain .ru (Poroshenko 2017), were closed down because they were part of Russia’s information warfare against Ukraine. President Zelenskyy (2020) extended these bans.
In southeastern Ukraine, only 4% watch Russian television. A mere 1% of Ukrainians younger than the age of 29 watch Russian television, and only 7% of young Ukrainians visit Russian websites (Zarembo 2017, 21). Facebook is now far more popular than VKontakte and, by 2020, 60% of Ukrainians used Facebook and only 7% used VKontakte (Sotsialno-politychna sytuatsiya v Ukrayini 2020). Western search engines such as Google Chrome are used far more often than Yandex,and Gmail has wiped out use of .ru.
Loss of Russian soft power and geopolitical influence is evident in religious affairs. All Ukrainian presidents (except Yanukovych) and every Ukrainian parliament supported autocephaly (independence) for Ukrainian Orthodoxy from the Russian Orthodox Church (Yushchenko 2008; Poroshenko 2018; Ukrainian Parliament 2016c; Ukrainian Parliament 2018). A 2018 opinion poll showed that Ukrainians supported religious independence from Moscow, with 52% believing that the pro-autocephalous Ukrainian Orthodox Church-Kyiv Patriarch was the historical successor to the Orthodox Church in Kyiv Rus. Only 12% believed that the Russian Orthodox Church to be the historical successor (Dynamics of the Patriotic Moods of Ukrainians 2018).
The Kyiv Metropolitan had been under the canonical jurisdiction of the Constantinople Patriarch until 1686, when Muscovy, sensing the weakness of Constantinople under Turkish occupation, illegally transferred the Ukrainian Church under the Moscow Patriarch. Until the seventeenth century, Belarus came under the Kyiv Metropolitan.
In October 2018, Constantinople Patriarch Bartholomew I declared the 1686 transfer to have been ‘uncanonical’ and returned Ukrainian Orthodox believers under Constantinople’s jurisdiction. In response, the Russian Orthodox Church broke off communications with the Constantinople Patriarch, and Putin called an emergency session of Russia’s Security Council. A March 2020 summit to condemn Ukrainian autocephaly showed the isolation of the Russian Orthodox Church when only three (Russia, Serbia, Jerusalem) of fourteen Orthodox Churches attended.
In January 2019, Bartholomew I issued a Tomos granting autocephaly to the Orthodox Church of Ukraine; following a merger between the Ukrainian Orthodox Church-Kyiv Patriarch, the Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox Church, and defectors from the Russian Orthodox Church in Ukraine. With 40% (12,000) of the total number of 30,000 Russian Orthodox Church parishes found in Ukraine, Ukraine’s autocephaly has dramatically reduced the influence of the Russian Orthodox Church inside Ukraine and in the broader Orthodox world. Russia is no longer the biggest Orthodox Church with the Romanian and Russian Orthodox Churches now approximately similar in size with 16,000 parishes each.
Russian soft power in Ukraine’s economy, trade, and energy has collapsed. Ukraine’s trade is individually higher with China (17.74%) and Germany (12.33%) than it is with Russia (10.94%), and trade with Poland (8.31%) is growing. Trade with the EU, which is now the biggest destination for Ukrainian exports, has grown from 26% to 47% since 2013. Ukraine is the third largest exporter of grain to the EU after the US and Brazil. In 2013, 29% of Ukrainian fruit and vegetables were exported to Russia which, by 2019, had collapsed to only 3.5%; the highest proportion is now exported to the EU (67%), the Middle East (14%), and Belarus (7%). Nicolai N. Petro (2016) and Mikhail Molchanov (2016, 2018) were wrong to believe that Ukraine would not survive economically without Russia.
For many Ukrainians, especially the younger generation, the negotiation of a visa-free regime with the EU, along with Ryan Air, Wizz Air, and other low-cost airlines, makes travel to the EU affordable. Since 2017, a quarter of Ukrainians have travelled visa-free to the EU. The highest numbers flying to the EU are from Kharkiv, Odesa, Lviv, and Kyiv oblasts (Getmanchuk and Litra 2019). Flights to Greece, the Czech Republic, and Germany have increased by 46%, 38%, and 31% respectively. Passenger traffic from Kyiv’s Borispil airport has more than doubled from 6 to 14 million, with similar high growth rates from Lviv, Zaporizhzhya, and Kharkiv airports.
Nearly as many Ukrainians travel into Russia (3.9 million) as travel to Hungary (3.4 million). Approximately 700,000 Ukrainians flew to Poland in 2019, up from 204,000 in 2017, facilitated by Ukrainians ability to fly to eight Polish cities from Kyiv’s two airports. Approximately 463,000 Ukrainians work permanently in Poland (representing three-quarters of foreign workers) together with one million Ukrainians who work temporarily and travel back and forth for trade. Approximately 25,000 Ukrainians study in Poland.
Odesa, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Lviv, and Sumy oblasts have high levels of participation in educational and cultural exchanges with the EU (Getmanchuk and Litra 2019). In comparison, in Russia and Belarus, which do not have visa-free regimes with the EU, only 12,000 Russians and 38,000 Belarusians work in Poland. Ukraine receives the largest remittances from abroad of any country in Europe, which amounted to $15.8 billion, or 10% of GDP, in 2019.
Since the introduction of a visa-free regime between Ukraine and the EU in 2017, a growing number of Ukrainians from its southeasternsoutheastern oblasts have travelled to Poland (Olearchyk 2019). The southern Ukrainian oblast of Mykolayiv has the highest indicator of European integration of any Ukrainian region (Getmanchuk and Litra 2019). The highest rates of European investment, and the largest number of projects funded by the European Investment Bank and European Bank for Reconstruction and Development are found in the southeastern Luhansk, Sumy, Donetsk, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Zaporizhzhya, Mykolayiv, and Kherson oblasts (Getmanchuk and Litra 2019).
Russian political influence through corrupt networks has declined since Autumn 2015, when Ukraine ended imports of Russian gas (Ukraine’s Fight Against Corruption: The Economic 2018). Since 2015, oligarchs have no longer been able to make huge profits from opaque gas intermediaries, using some of these funds to finance pro-Russian political forces, such as the Party of Regions. Gas tycoon Dmytro Firtash is fighting extradition to the US on charges of corruption and to Spain over collusion with Russian organised crime. With the loss of corrupt rents from the gas trade, Ukraine’s pro-Russian Opposition Platform-For Life is completely reliant on Russian funding through Medvedchuk, Putin’s representative in Ukraine. With the disappearance of Ukraine’s ‘east,’ this reduces its attractiveness to voters even further.
Russia’s attempt to bypass Ukraine with Nord Stream II were thwarted by US sanctions, forcing Putin to agree to a five-year transit agreement for gas through Ukraine beginning in January 2020. Ukraine’s energy needs are met by importing gas from central Europe and, since 2019, US liquefied natural gas and oil transported through Poland. Ironically, Putin’s military aggression has been a decisive factor in making Ukraine energy independent of Russia.
Prospects for Peace
In an environment where the rule of law is non-existent and is always flouted at home and abroad, it is unsurprising that treaties and agreements signed by Ukraine with Russia were worthless pieces of paper during the 2014 crisis. This has increased Ukrainian distrust in Putin’s promises. D’Anieri (2019, 258) writes that the 1997 Russian-Ukrainian treaty ‘brought little in the way of friendship, opposed as it was by many Russian elites and the treaty ‘had little impact on Ukrainian-Russian relations.’ Russia had ‘deep and fundamental’ disagreements over Ukraine and always insisted that Moscow ‘considered a voice in Ukraine as essential’ (D’Anieri 2019, 258–259).
Democracy and geopolitics first merged in the Orange Revolution and, since then, ‘Ukraine’s conflict with Russia and the West’s conflict with Russia were tightly bound together’ (D’Anieri 2019, 137). The Orange Revolution ‘changed everything’ because ‘the two conflicts have become one’ (D’Anieri 2019, 137). Ukraine’s democratisation signifies the enlargement of western influence into what Russia views as its exclusive sphere of influence. Ukraine’s European integration was unacceptable to Russia in 2014, and this remains true today.
- Russian and Russian Proxy Forces in Crimea and the Donbas[3]
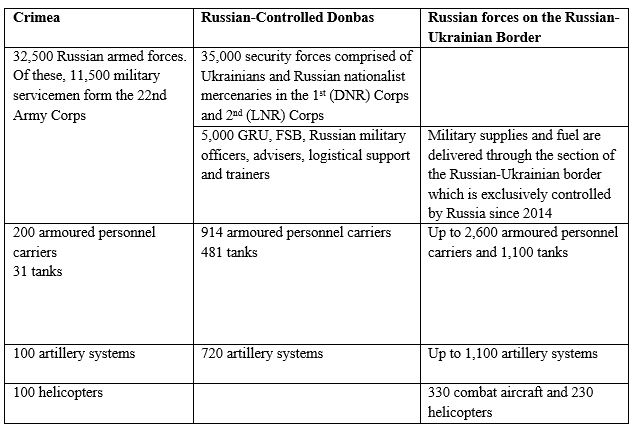
Ukraine would have to agree to many Russian demands to achieve peace, which would be tantamount to capitulation for many Ukrainians. These demands include relinquishing sovereignty over Crimea and changing its constitution to provide ‘special status’ to the DNR and LNR. Russia demands that the 35,000-strong security forces of the DNR and LNR be re-organised into a local militia, which would amount to the legalisation of Russian-controlled forces. Ukraine demands the de-militarisation and withdrawal of all foreign forces, but it is impossible for a withdrawal to take place as long as Russia sticks to the fiction that it has no security forces in the Donbas. Russia has also rejected returning control over the border to Ukraine until Ukraine meets all of its demands.
Russia seeks a neutral Ukraine that relinquishes its goal of joining NATO and the EU, two objectives that are enshrined in Ukraine’s constitution since February 2019. Changing the constitution requires a majority two-thirds vote by parliament, which would be impossible and is opposed by large majorities of Ukrainians, who now support membership in both organisations. Support for NATO membership has skyrocketed since 2014 and a high majority would support membership in a referendum. Approximately 69% of Ukrainians would participate in a referendum on NATO membership, of whom 70% would vote in favour, up from 66% in 2017 (Pidsumky-2018: hromadska dumka 2018). In Ukrainian-controlled Donbas, 31% of people support NATO membership, despite miniscule support prior to 2014 (Observations of Public Attitudes in Donbas 2020).
One of Zelenskyy’s election promises was to bring peace to the Donbas, and he remained naively confident in pushing the peace process forward during his first year in office (see Kuzio 2020b). President Zelenskyy’s inability to move the peace process forward confirms that neither President Poroshenko nor ‘Ukrainian nationalists’ were the obstacles. Zelenskyy’s decision to withdraw from three contact points on the front line was unpopular. With Russian and Russian proxy forces continuing to engage Ukrainian forces on a daily basis, the withdrawals failed to achieve a significant reduction in hostilities.
Zelenskyy also oversaw two prisoner exchanges, which earned him good will as a populist exercise, but also criticism. Of those transferred to Russia, six prisoners were Berkut riot police guilty of killing protestors during the Euromaidan. Another was Volodymyr Tsemakh, who had been kidnapped by Security Service of Ukraine special forces in a daring raid and was wanted by the Hague-based Joint Investigations Team due to his involvement in the downing of MH17.
Despite his good will and willingness to compromise, Zelenskyy was unable to achieve any major success in the peace process for reasons which are the same as those under Poroshenko. An inability to push the peace process forward points to deeper issues; after all, Zelenskyy is a centrist, Russian-speaking politician from eastern Ukraine who (unlike his predecessor) would have been willing to make difficult compromises. Typically, in Russian policies towards Ukraine, Putin does not attempt to engage with Zelenskyy or adopt compromises, in this case towards the goal of achieving peace. Russian demands towards Kyiv are not modified and Zelenskyy is simply expected to abide by them.
In April 2019, the month Zelenskyy was elected, Putin slapped him twice in the face. Russia began issuing passports to residents of Russian-controlled Donbas, forecasting that, by the end of 2020, one million residents of the DNR and LNR would possess them. The residents of Russian-controlled Donbas returned their gratitude and voted for constitutional amendments in the July 2020 Russian referendum. In the same month, Russia introduced sanctions on 140 goods (on top of the 200 goods sanctioned by Russia earlier in December 2018), including coal, crude oil, and oil products, which could no longer be exported to Ukraine.
Conclusion
Stereotypes of a divided Ukraine on the verge of disintegration, and Ukrainians and Russians as very close people were wrong prior to 2014 and are outdated in the face of the tectonic changes that have occurred since then (see Kuzyk 2019). While Ukraine has been removed from the Russian Orthodox Church’s canonical territory, Ukraine remains ‘Russian territory’ for western historians of ‘Russia,’ who did not change their approach following the emergence of independent Russia and Ukraine. This makes this author sceptical that they will take into account the impact of the Russian-Ukrainian War and Ukrainian Orthodox autocephaly on the writing of ‘Russian’ history.
Putin’s rehabilitation of Tsarist Russian and White émigré views, which deny the existence of a Ukrainian people and portray Ukraine as an ‘artificial’ and failed state, annexation of Crimea, and invasion and war with Ukraine have fundamentally changed the Ukrainian-Russian relationship. A pro-Russian ‘east’ has disappeared, Ukrainians no longer view Russians as their ‘brothers,’ and Russian soft power in Ukraine has disintegrated. Ukrainian opinion polls show dramatic changes in identity, views of Ukrainian history and relations with Russia.
D’Anieri (2019) believes that the West’s goals of seeking to keep Russia satisfied and Ukraine independent are mutually incompatible. NATO is not Russia’s only problem; a democratising Ukraine integrating into Europe within the EU’s Eastern Partnership is also unacceptable to Russia. Putin does not distinguish between integration (on offer in the Eastern Partnership) and membership (which is not). Integration into Europe means that Putin cannot fulfil his destiny of ‘gathering Russian lands’ because Ukraine would not be part of the Russian World. Russian leaders believe that ‘Russian lands,’ wrongly included in Ukraine, are being prevented from joining the Russian World by Galician Ukrainian nationalists. Russian leaders have continued to believe this fallacy after Zelenskyy’s election.
With Russian nationalism (imperialism) driving Putin’s policies towards Ukraine, it is difficult to see how peace in the Donbas can be achieved. With Putin in power for another 16 years, the policies he has pursued, however counter-productive they have been to Russian goals, will continue towards Ukraine.
[1] See photos and video footage of 20,000 veterans marching in Kyiv on Independence Day on 24 August 2020.
[2] Dionizy Garbacz, Wołyniak, legenda prawdziwa (Warsaw: Polish Institute of National Remembrance, 2015). https://ipn.poczytaj.pl/ksiazka/wolyniak-legenda-prawdziwa-cd-dionizy-garbacz,72549
Further Reading on E-International Relations
- Opinion – Russia’s Choices in Ukraine
- Opinion – Signed, Sealed and Irrelevant: The Impact of the Budapest Memorandum
- Applying Just War Theory to the Russo-Ukrainian War
- Opinion – The Impact of the Russia-Ukraine War on European Nationalism
- Why Both Ukraine and Russia Need Peace after a Third Summer of War
- Opinion – A Hidden Victory? The Winter War and Russia’s Invasion of Ukraine